
Comparison of microfiber concrete and conventional concrete
Modern construction technologies allow for the creation of more durable and resilient structures. One such solution is the use of concrete with microfibers. Adding fibers significantly enhances the material's properties compared to ordinary concrete. In this article, we will examine the differences, advantages, and applications of microfiber concrete in detail, as well as the role of polypropylene fiber for concrete.
What is microfiber concrete
Microfiber concrete is a mixture of cement, sand, gravel, and specially added very fine fibers. These fibers can be synthetic (polypropylene) or metallic. The main purpose of microfibers is to reduce shrinkage cracks and increase the concrete's resistance to mechanical stress.
The fibers are evenly distributed throughout the mixture, creating a reinforcing framework at the micro-level. This significantly extends the lifespan of structures and reduces the risk of damage.

Advantages of microfiber concrete
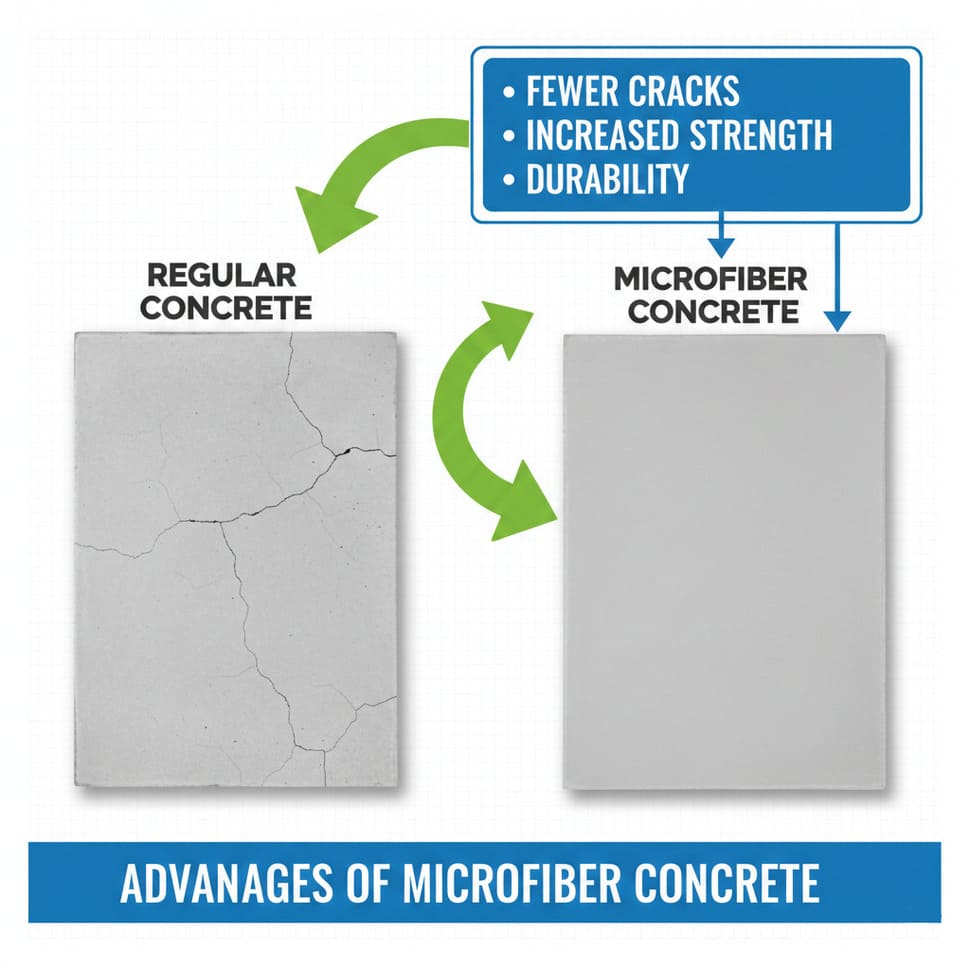
Using microfibers provides numerous benefits that make concrete more reliable and durable:
- Reduction of shrinkage cracks due to even stress distribution throughout the volume.
- Increased tensile and flexural strength.
- Improved impact resistance and vibration resilience.
- Shorter preparation time for structures to be operational.
- Enhanced adhesion to reinforcing elements, which is especially important for screeds and industrial floors.
Even a small amount of microfibers significantly improves the concrete's strength, making it more resistant to external loads.
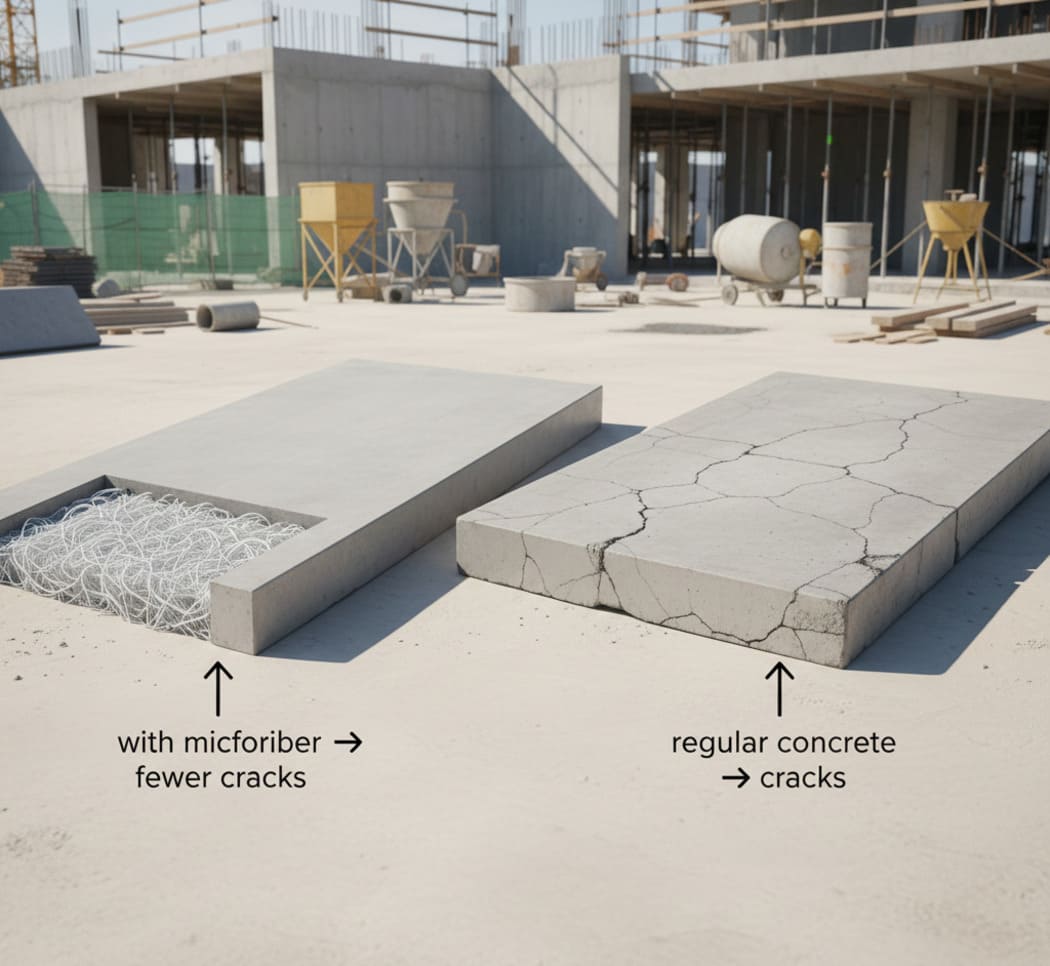
Differences from ordinary concrete
Ordinary concrete without additives is also reliable and strong, but it is more prone to cracking and damage under dynamic loads. The main disadvantages of ordinary concrete are:
- Prone to shrinkage cracks during drying.
- Limited impact resistance and flexibility.
- Often requires additional reinforcement to reduce the risk of failure.
Adding microfibers minimizes these drawbacks and increases the durability of the structure.
Comparison of concrete properties
| Property | Microfiber Concrete | Ordinary Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Shrinkage cracks | Minimal | High |
| Tensile strength | Increased | Standard |
| Impact resistance | High | Medium |
| Preparation time for use | Shorter | Longer |
| Durability | Higher | Standard |
| Need for additional reinforcement | Partially not required | Often required |
As can be seen, microfiber concrete outperforms ordinary concrete in most key parameters, especially in durability and resistance to cracking.
Polypropylene fiber for concrete
One of the most popular types of microfibers is polypropylene fiber for concrete. It has several advantages:
- Does not corrode, unlike metallic fibers.
- Reduces shrinkage cracks and increases mixture strength at the micro-level.
- Easy to dose and evenly distributes throughout the concrete mass.
Using polypropylene fiber makes concrete stronger and more durable, especially for screeds, industrial floors, and outdoor structures. More about its applications and properties can be found on the MixFiber website.
Applications of microfiber concrete
Microfiber concrete is widely used in construction:
- Floor screeds and industrial coatings.
- Outdoor structures exposed to temperature fluctuations.
- Bridges, tunnels, and road surfaces.
- Decorative panels and architectural elements.
Thanks to its improved properties, such concrete ensures structural reliability and reduces maintenance costs.
Usage tips
For maximum effect of microfibers, it is recommended to:
- Mix fibers evenly with the dry mixture before adding water.
- Use the correct amount of fibers according to the type of structure.
- Ensure uniform fiber distribution throughout the concrete volume.
Following these guidelines ensures stable material properties and long-lasting structures.
Recommended products
 |  |
| Armotec Fibre | Fibermix Microfiber |